(Bold text = submission by CCAP staff or collaborators)
Note: for strains where we have DNA barcodes we can be reasonably confident of identity, however for those not yet sequenced we rely on morphology
and the original identification, usually made by the depositor. Although CCAP makes every effort to ensure the correct taxonomic identity of strains, we cannot guarantee
that a strain is correctly identified at the species, genus or class levels. On this basis users are responsible for confirming the identity of the strain(s) they receive
from us on arrival before starting experiments.
For strain taxonomy we generally use AlgaeBase for algae and
Adl et al. (2019) for protists.
| Attributes | |
| Authority | (Kuckuck) Gallardo 1992 |
| Isolator | Müller (1978) |
| Collection Site | intertidal mud Beaufort, vicinity of Duke Marine Station, North Carolina, USA |
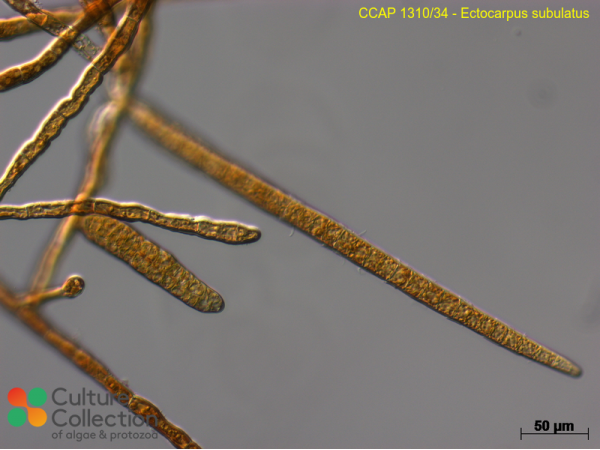
| Notes | field-collected male gametophyte; ITS phylogenetic studies show that this strain belongs to sub group 2d in the publication Stache-Crain et al (1997), for which Peters et al (2015) have reinstated the name Ectocarpus subutulus (Kützung). This species represents a subgroup of Ectocarpus which can tolerate low salinity and high temperatures. Stache-Crain B, Müller DG & Goff LJ (1997) Molecular systematics of Ectocarpus and Kuckuckia (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae) inferred from phylogenetic analysis of nuclear- and plastid-encoded DNA sequences. J. Phycol. 33 152-168. Peters AF, Couceiro L, Tsiamis K, Küpper FC & Valero M. (2015) Barcoding of cryptic stages of marine brown algae isolated from incubated substratum reveals high diversity in Acinetosporaceae (Ectocarpales, Phaeophyceae). Cryptogamie, Algologie 36(1) 3-29; This macroalgal culture contains bacteria and probably other organisms in low numbers, we are happy to provide further info on specific strains if you contact us; name changed Mar23 as per AlgaeBase |
| Axenicity Status | Bacteria and other organisms present |
| Area | North America |
| Country | USA |
| Environment | Marine |
| GMO | No |
| Group | Macroalgae |
| In Scope of Nagoya Protocol | No |
| ABS Note | Collected pre Nagoya Protocol. No known Nagoya Protocol restrictions for this strain. |
| Collection Date | c 1978 |
| Original Designation | Ec sil Bft 15b m |
| Pathogen | Not pathogenic: Hazard Class 1 |
| Strain Maintenance Sheet | SM_Ectocarpus.pdf |
| Toxin Producer | Not Toxic / No Data |
| Type Culture | No |
| Taxonomy WoRMS ID | 550728 |
| Equivalent Strains | KU-MACC 1330 |
| Other Designations | DGM 014-06 |
| Synonyms | Ectocarpus subulatus |
| Formerly Listed in CCAP as | Ectocarpus siliculosus (Dilwyn) Lyngbye 1819,Ectocarpus sp.,Ectocarpus subulatus |
CCAP 1310/34
Ectocarpus siliculosus var. dasycarpus
- Product Code: CCAP 1310/34
- Availability: See Availability/Lead Times
Related Products
CCAP MAMP-C
Modified Provasoli's Medium
STERILE STOCKS
Sterile concentrated stock to make up 5 litres of Modified Provasoli's medium (or 10 litres of half-
CCAP MAMP-P
Modified Provasoli's Medium
1 LITRE PREMADE
1 litre of sterile, ready to use, Modified-Provasoli's medium (full strength). Modified Provasoli's